Contents
Creating an inhomogeneous medium: inhomogeneous.m
This example demonstrates how define inhomogeneous optical properties
xsize = 10; % width of the region [mm] ysize = 10; % height of the region [mm] dh = 1; % discretisation size [mm] vmcmesh = createRectangularMesh(xsize, ysize, dh);
Give varying optical parameters
% Set constant background coefficients vmcmedium.absorption_coefficient = 0.01; % absorption coefficient [1/mm] vmcmedium.scattering_coefficient = 1.0; % scattering coefficient [1/mm] vmcmedium.scattering_anisotropy = 0.9; % anisotropy parameter g of % the Heneye-Greenstein scattering % phase function [unitless] vmcmedium.refractive_index = 1.3; % refractive index [unitless] % Resize the fields in vmcmedium so that they match the number of elements in the mesh vmcmedium = createMedium(vmcmesh,vmcmedium); % Select elements from the mesh radius = 2.5; % [mm] centercoord = [0.0 0.0]; % [mm] elements_of_the_circle = findElements(vmcmesh, 'circle', centercoord, radius); % Assign a unique absorption coefficient to the selected elements vmcmedium.absorption_coefficient(elements_of_the_circle) = 0.25;
Plot the parameter distribution
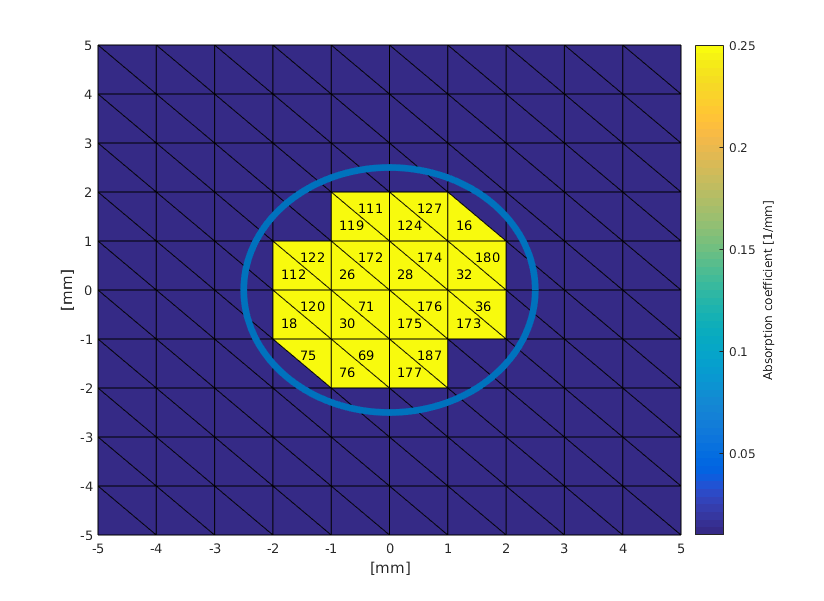
The resulting absorption coefficient distribution is shown in the figure below. Shown is also the circle that was used to select the elements.
Note that some triangles intersect the circle, resulting in a poor representation of the circular shape. The representation can be improved by a better mesh or by incresing the discretisation size.
Create a light source
vmcboundary.lightsource(4:7) = {'cosinic'};
Run the Monte Carlo simulation
solution = ValoMC(vmcmesh, vmcmedium, vmcboundary);
ValoMC-2D -------------------------------------------- Version: v1.0b-118-g853f111 Revision: 131 OpenMP enabled Using 16 threads -------------------------------------------- Initializing MC2D... Computing... ...done Done
Plot the solution
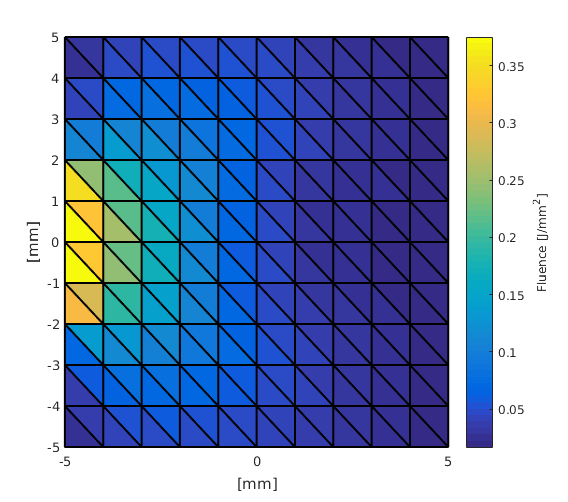
Note how the area with the higher absorption coefficient affects the fluence distribution (c.f. 'Simple Example')
hold on; patch('Faces',vmcmesh.H,'Vertices',vmcmesh.r,'FaceVertexCData', solution.element_fluence, 'FaceColor', 'flat', 'LineWidth',1.5); xlabel('[mm]'); ylabel('[mm]'); c = colorbar; % create a colorbar c.Label.String = 'Fluence [J/mm^2]'; hold off